B. pertussis and pertussis toxin have been used for more than 50 years to induce neuropathology in the primary animal model of MS, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. ILiAD is researching the potential of nasal B. pertussis colonization to induce neuroantigen sensitization and neuropathology, and the ability of our technology to prevent such disease.
In addition to noting the concurrent decades-long rise in rates of B. pertussis and celiac disease in the United States, we have published on the extraordinary covariation between rates of celiac disease in Swedish children and the incidence of whooping cough in Sweden at the end of the last century. Evidence suggests that B. pertussis colonization may induce mucosal sensitization to co-localized gliadin in the nasopharynx and play a major unrecognized role in the onset of celiac disease.
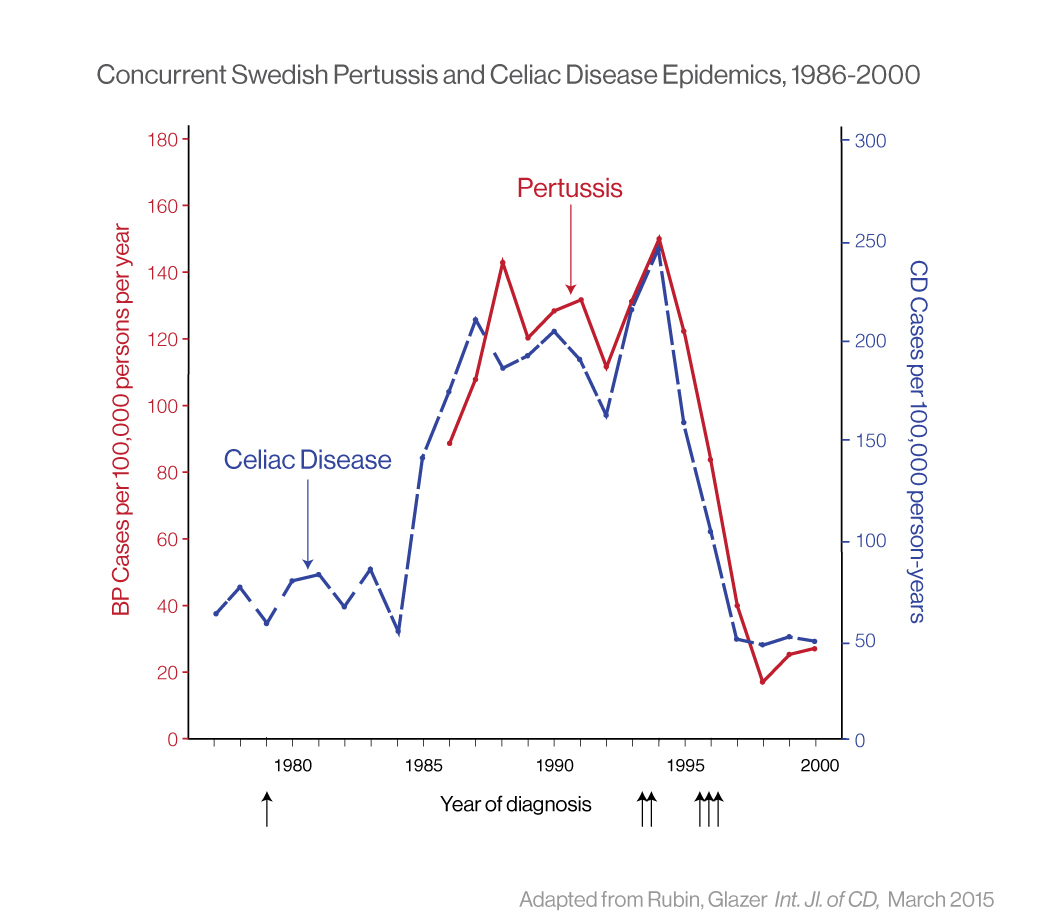
The cessation of B. pertussis immunization in Sweden in 1979 (↑) preceded a rise in B. pertussis in the 1980s, persisting until acellular B. pertussis vaccination trials in 1993-1994 (↑↑) and broad implementation of B. pertussis vaccination in 1996 (↑↑↑) (red line). The incidence of CD in Swedish children < 2 years of age, based on data from Olsson et al. (dashed blue line), closely tracks pertussis incidence in Sweden during this period.